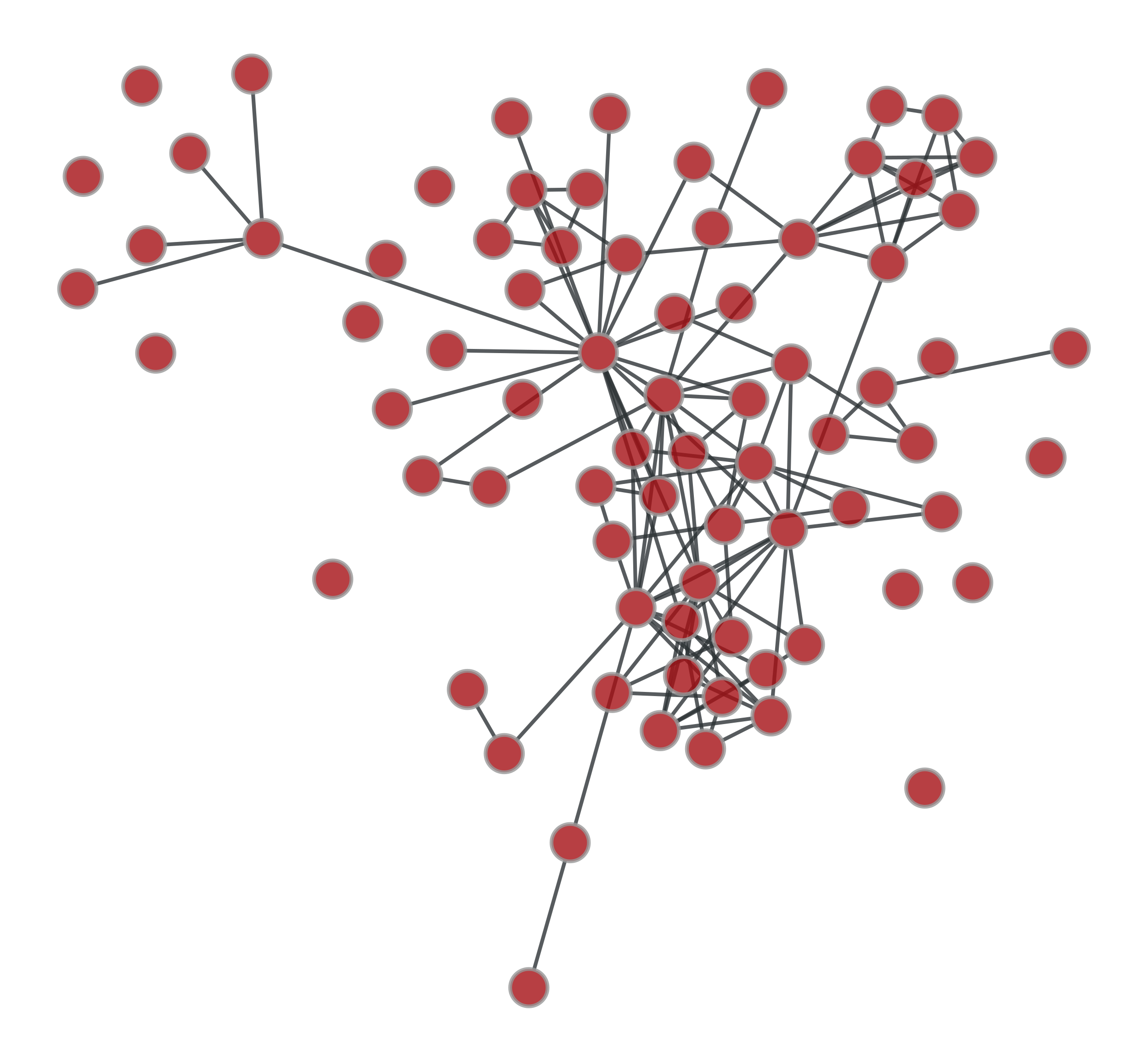
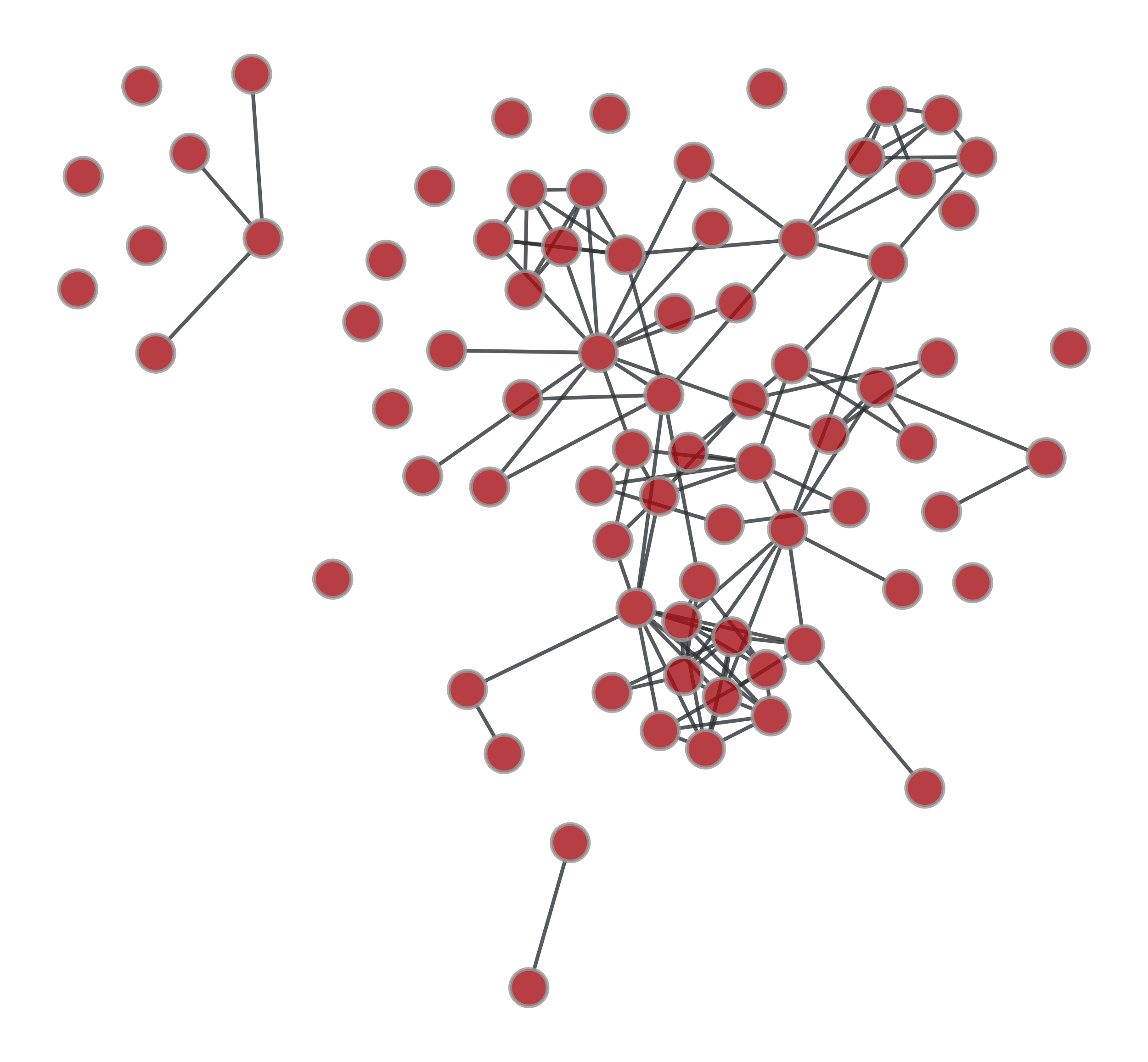
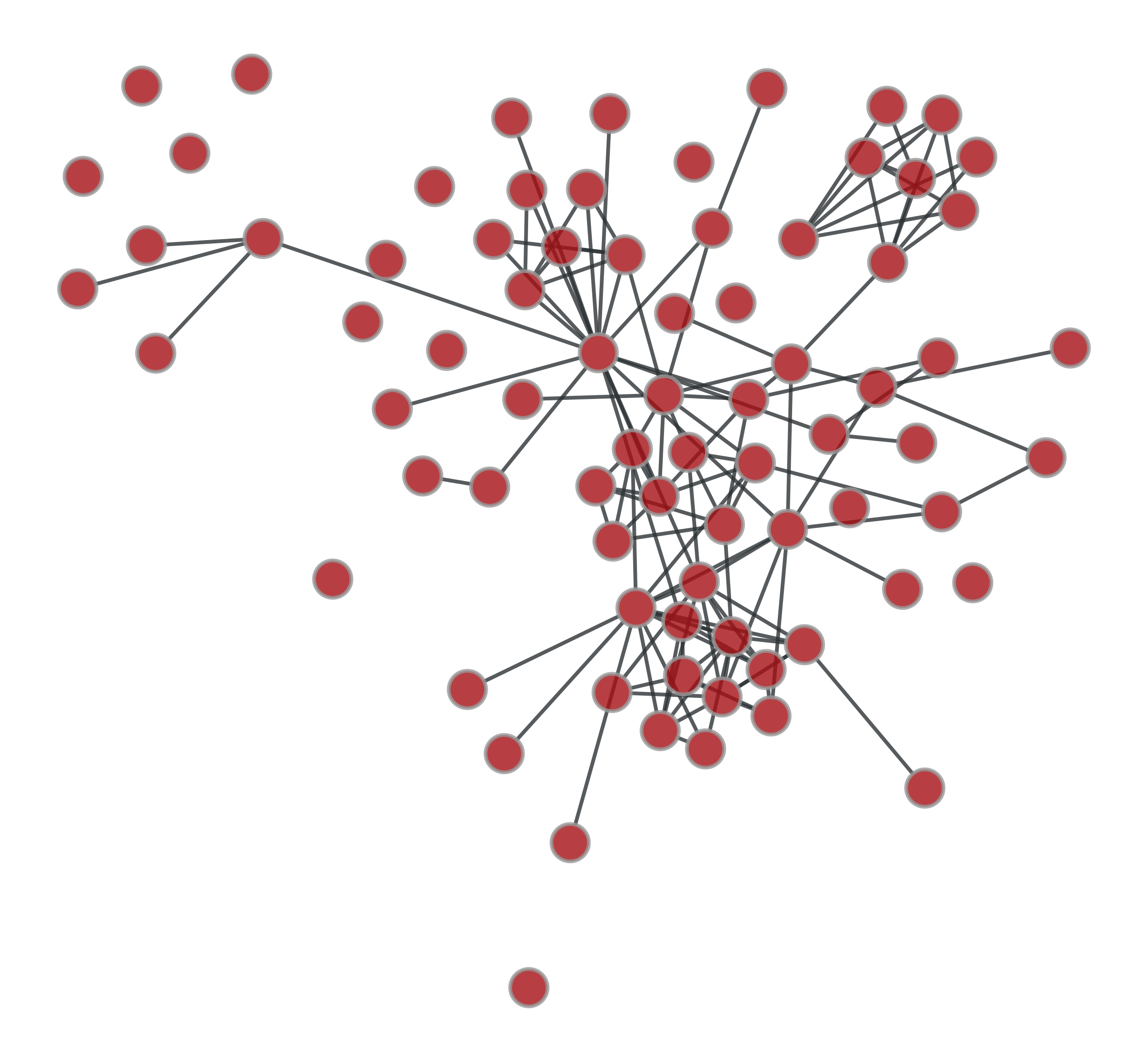
graph_sym_difference#
- graph_tool.generation.graph_sym_difference(g1, g2, eweight1=None, eweight2=None, vmap='identity', props=[], mt='set', internal_props=False, in_place=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Return a graph containing the symmetric difference of the edges of graphs
g1andg2.- Parameters:
- g1
Graph Graph to be merged into.
- g2
Graph Graph to be merged from.
- eweight1
EdgePropertyMap(optional, default:None) If provided, this will determine the weights of the edges of graph
g1. If not provided, each edge will be assumed to have unity weight.- eweight2
EdgePropertyMap(optional, default:None) If provided, this will determine the weights of the edges of graph
g2. If not provided, each edge will be assumed to have unity weight.- vmap
VertexPropertyMap,"identity", orNone(optional, default:None) Vertex property map owned by
g2which maps each of its vertices to vertex indices belonging tog1, in which case they are considered to be identical. Negative values mean no mapping exists, and thus both vertices ing1andg2will be present in the difference graph. If this argument is not provided (i.e.vmapisNone), both vertex sets will be added to the difference. Ifvmapisg2.vertex_index, and the vertex indexes are identical in both graphs, the difference will correspond only to the edge sets. A special value ofvmap == "identity"is a shortcut forvmap = g2.vertex_index.- propslist of tuples of
PropertyMap(optional, default:[]) Property maps to be included in the difference. Each element of th list must be a pair of
PropertyMapobjects. The first element must be a property ofg1, and the second ofg2. If either value isNone, an new map will be created, and set to appropriately empty values.- mt
str(otional, default:"set") Merge rule for property values. Should be one of
"set","sum","diff","idx_inc","append","concat". Seegraph_merge()for further documentation.- internal_props
bool(optional, default:False) If
Trueall internal property maps ofg1andg2will be included in the difference.- in_place
bool(optional, default:False) If
True, the symmetric difference is computed in-place intog1, which is then modified. IfFalse, a new graph is created, and both graphs remain unmodified.- **kwargs
dict(optional, default:{}) Remaining keyword parameters will be forwarded to
graph_merge().
- g1
- Returns:
- ug
Graph The symmetric difference graph.
- w
EdgePropertyMap The edge weights of the difference graph. This is only returned if
eweight1is notNone.- propslist of
PropertyMapobjects List of properties in the difference graph. This is only returned if props is not empty. Internal property maps are not included in this list.
- ug
See also
graph_mergeMerge the edge sets between two graphs.
graph_unionUnion of the edge sets between two graphs.
graph_differenceDifference of the edge sets between two graphs.
graph_intersectionIntersection of the edge sets between two graphs.
Notes
This algorithm is a wrapper around
graph_merge(), and shares with it the same algorithmic complexity.Parallel implementation.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm will run in parallel using OpenMP. See the parallel algorithms section for information about how to control several aspects of parallelization.
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.ns["lesmis"] >>> u1 = gt.GraphView(g, efilt=np.random.random(g.num_edges()) < .5) >>> u2 = gt.GraphView(g, efilt=np.random.random(g.num_edges()) < .5) >>> u = gt.graph_sym_difference(u1, u2) >>> gt.graph_draw(u1, pos=g.vp._pos, output="u1.pdf") <...> >>> gt.graph_draw(u2, pos=g.vp._pos, output="u2.pdf") <...> >>> gt.graph_draw(u, pos=g.vp._pos, output="gsdiff.pdf") <...>