push_relabel_max_flow#
- graph_tool.flow.push_relabel_max_flow(g, source, target, capacity, residual=None)[source]#
Calculate maximum flow on the graph with the push-relabel algorithm.
- Parameters:
- g
Graph Graph to be used.
- sourceVertex
The source vertex.
- targetVertex
The target (or “sink”) vertex.
- capacity
EdgePropertyMap Edge property map with the edge capacities.
- residual
EdgePropertyMap(optional, default: none) Edge property map where the residuals should be stored.
- g
- Returns:
- residual
EdgePropertyMap Edge property map with the residual capacities (capacity - flow).
- residual
Notes
The algorithm is defined in [goldberg-new-1985]. The complexity is \(O(V^3)\).
References
[boost-push-relabel]http://www.boost.org/libs/graph/doc/push_relabel_max_flow.html
[goldberg-new-1985]A. V. Goldberg, “A New Max-Flow Algorithm”, MIT Tehnical report MIT/LCS/TM-291, 1985.
Examples
>>> g = gt.load_graph("flow-example.xml.gz") >>> cap = g.edge_properties["cap"] >>> src, tgt = g.vertex(0), g.vertex(1) >>> res = gt.push_relabel_max_flow(g, src, tgt, cap) >>> res.a = cap.a - res.a # the actual flow >>> max_flow = sum(res[e] for e in tgt.in_edges()) >>> print(max_flow) 44.8905957841... >>> pos = g.vertex_properties["pos"] >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=pos, edge_pen_width=gt.prop_to_size(res, mi=0, ma=5, power=1), output="example-push-relabel.pdf") <...>
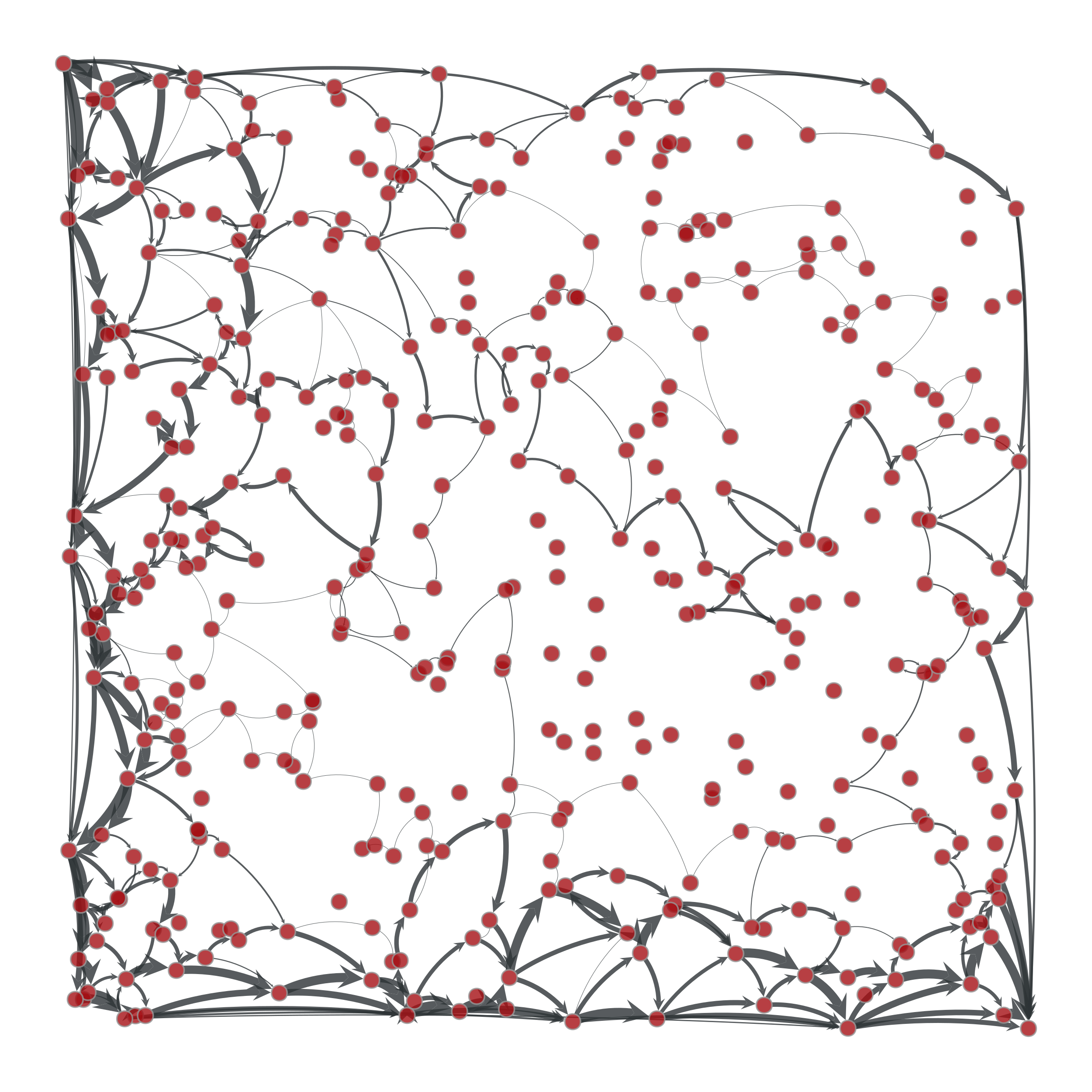
Edge flows obtained with the push-relabel algorithm. The source and target are on the upper left and lower right corners, respectively. The edge flows are represented by the edge width.#