condensation_graph#
- graph_tool.generation.condensation_graph(g, prop, vweight=None, eweight=None, aprops=None, parallel_edges=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Obtain the condensation graph, where each vertex with the same ‘prop’ value is condensed in one vertex.
- Parameters:
- g
Graph Graph to be modelled.
- prop
VertexPropertyMap Vertex property map with the community partition (needs to be integer-valued).
- vweight
VertexPropertyMap(optional, default: None) Vertex property map with the optional vertex weights.
- eweight
EdgePropertyMap(optional, default: None) Edge property map with the optional edge weights.
- apropslist of
VertexPropertyMap(optional, default: None) If provided, the sum of each property map in this list for each vertex or edge in the condensed graph will be computed and returned.
- parallel_edges
bool(optional, default:False) If
True, parallel edges will be included in the condensation graph, such that the total number of edges will be the same as in the original graph.
- g
- Returns:
- condensation_graph
Graph The community network
- vcount
VertexPropertyMap A vertex property map with the vertex count for each community.
- ecount
EdgePropertyMap An edge property map with the inter-community edge count for each edge.
- propslist of
PropertyMap A list of property maps with summed values of the properties passed via the
apropsparameter.
- condensation_graph
See also
graph_mergeMerge the edge sets between two graphs.
Notes
Each vertex in the condensation graph represents one community in the original graph (vertices with the same ‘prop’ value), and the edges represent existent edges between vertices of the respective communities in the original graph.
This algorithm is a wrapper around
graph_merge(), and shares with it the same algorithmic complexity.Parallel implementation.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm will run in parallel using OpenMP. See the parallel algorithms section for information about how to control several aspects of parallelization.
Examples
Let’s first obtain the best block partition with
B=5.>>> g = gt.collection.data["polbooks"] >>> # fit a SBM >>> state = gt.BlockState(g) >>> gt.mcmc_equilibrate(state, wait=1000) (...) >>> b = state.get_blocks() >>> b = gt.perfect_prop_hash([b])[0] >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=b, vertex_shape=b, ... output="polbooks_blocks_B5.pdf") <...>
Now we get the condensation graph:
>>> bg, vcount, ecount, props = \ ... gt.condensation_graph(g, b, aprops=[g.vp["pos"]]) >>> pos = props[0] >>> for v in bg.vertices(): ... pos[v].a /= vcount[v] >>> gt.graph_draw(bg, pos=pos, vertex_fill_color=bg.vertex_index, ... vertex_shape=bg.vertex_index, ... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(vcount, mi=40, ma=100), ... edge_pen_width=gt.prop_to_size(ecount, mi=2, ma=10), ... fit_view=.8, output="polbooks_blocks_B5_cond.pdf") <...>
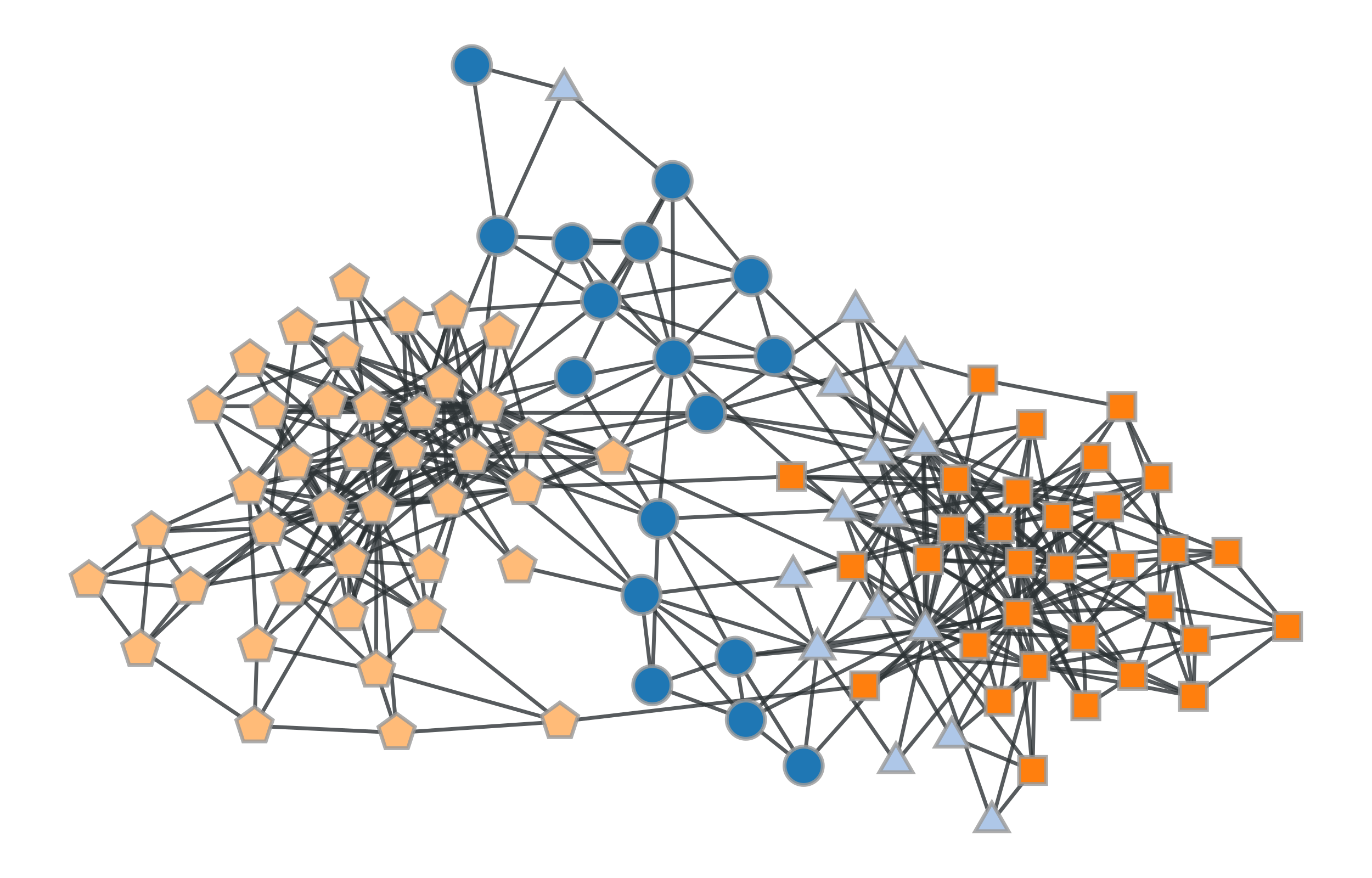
Block partition of a political books network with \(B=5\).#
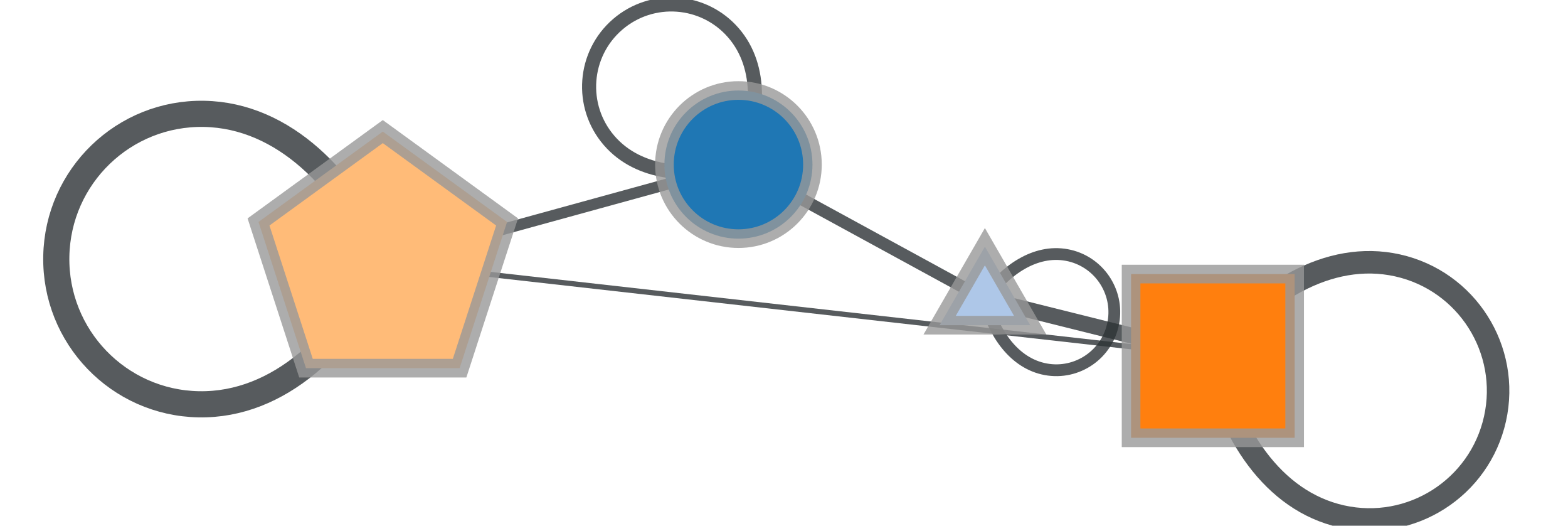
Condensation graph of the obtained block partition.#