minimize_nested_blockmodel_dl#
- graph_tool.inference.minimize_nested_blockmodel_dl(g, init_bs=None, state=<class 'graph_tool.inference.nested_blockmodel.NestedBlockState'>, state_args={}, multilevel_mcmc_args={})[source]#
Fit the nested stochastic block model, by minimizing its description length using an agglomerative heuristic.
- Parameters:
- g
Graph The graph.
- init_bsiterable of iterable of
int``s (optional, default: ``None) Initial hierarchical partition.
- stateSBM state class (optional, default:
NestedBlockState) Type of model that will be used.
- state_args
dict(optional, default:{}) Arguments to be passed to appropriate state constructor (e.g.
BlockState)- multilevel_mcmc_args
dict(optional, default:{}) Arguments to be passed to
multilevel_mcmc_sweep().
- g
- Returns:
- min_statetype given by parameter
state State with minimum description length.
- min_statetype given by parameter
Notes
This function is a convenience wrapper around
multilevel_mcmc_sweep().See [peixoto-hierarchical-2014] for details on the algorithm.
This algorithm has a complexity of \(O(E \ln^2 V)\), where \(E\) and \(V\) are the number of edges and nodes in the network, respectively.
References
[peixoto-hierarchical-2014]Tiago P. Peixoto, “Hierarchical block structures and high-resolution model selection in large networks “, Phys. Rev. X 4, 011047 (2014), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.4.011047 [sci-hub, @tor], arXiv: 1310.4377.
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["power"] >>> state = gt.minimize_nested_blockmodel_dl(g) >>> state.draw(output="power_nested_mdl.pdf") (...)

Hierarchical Block partition of a power-grid network, which minimizes the description length of the network according to the nested (degree-corrected) stochastic blockmodel.#
>>> g = gt.collection.data["celegansneural"] >>> state = gt.minimize_nested_blockmodel_dl(g, state_args=dict(overlap=True)) >>> state.draw(output="celegans_nested_mdl_overlap.pdf") (...)
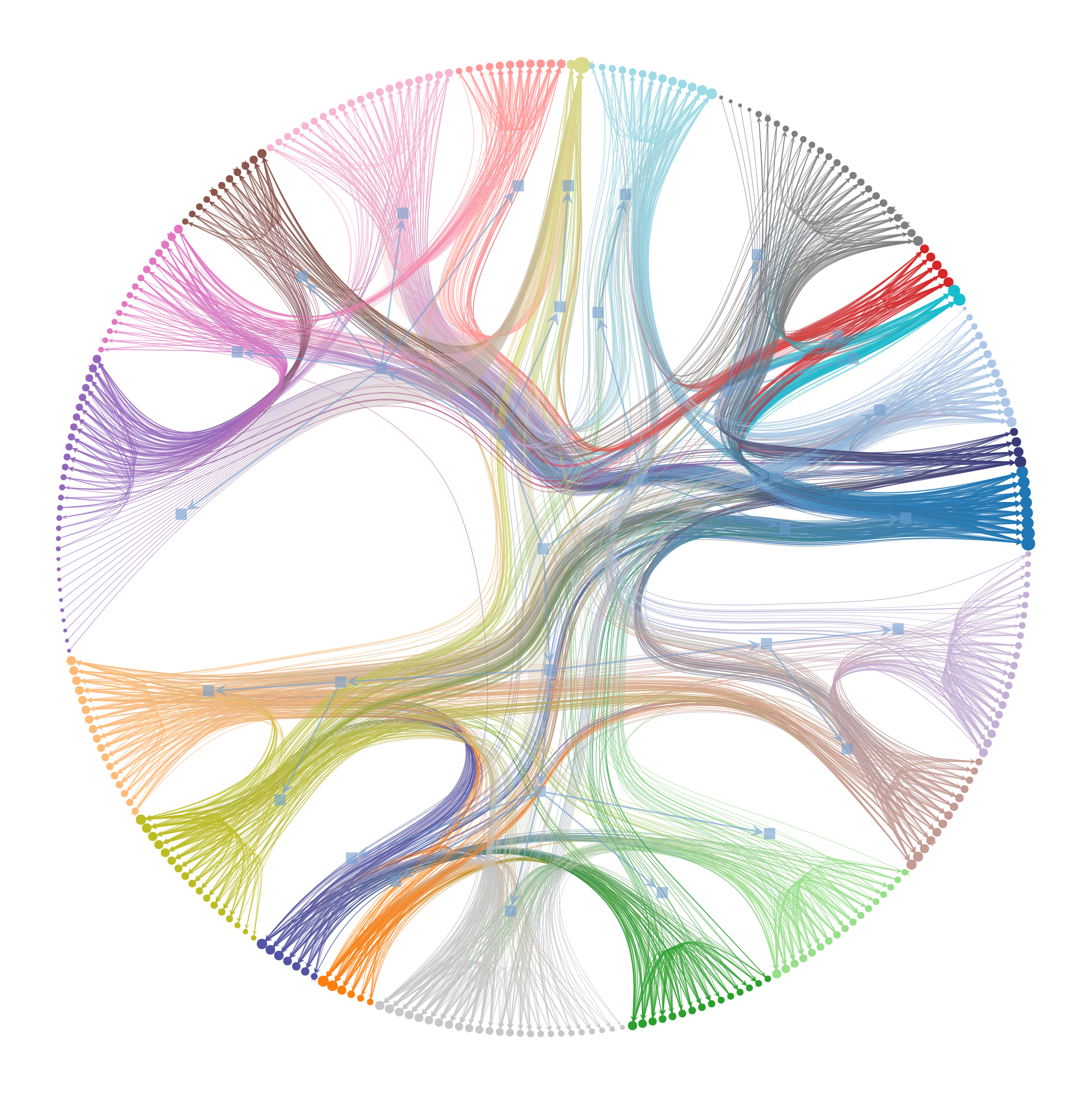
Overlapping block partition of the C. elegans neural network, which minimizes the description length of the network according to the nested overlapping degree-corrected stochastic blockmodel.#